Successful product design requires strategic vision, accurate research, and technical skill. This fascinating discipline is ripe for modernization. Keep reading to find out where the transformation is coming from and what the benefits are.
What is product design?
Product design is the process behind the creation of successful products or services. This process can be applied to both tangible products and intangible services, from software to automotive design, consumer goods, etc.
The ultimate goal of this process is to create solutions that embody the following criteria:
- Top functionality
- An excellent user experience
- High appeal
- Clear value
- Strong recognition / differentiation
- Profitability
In short, product design seeks to deliver maximum value.
This process also emphasizes performance, in two aspects:
- The performance of the product itself
- How it performs in the marketplace over time
Designing a product involves extensive fine tuning of a concept to ensure it consistently delivers top performance in these two areas. This requires the ability to anticipate future market conditions and to ensure that the final product satisfies them.
Key steps in product design
This concept extends along the entire product development process. There isn’t a standard number of steps, as these may vary from industry to industry. But generally speaking, product design involves:
- Discovery / research: identifying user needs/behavior, determining target performance goals, etc.
- Definition / ideation (brainstorming, specifying success metrics, allocating time and resources to the project, etc.)
- Prototyping: following a design rationale and documenting design decisions while collaboratively creating the prototype.
- Reviewing to identify areas of improvement.
- Final product creation.
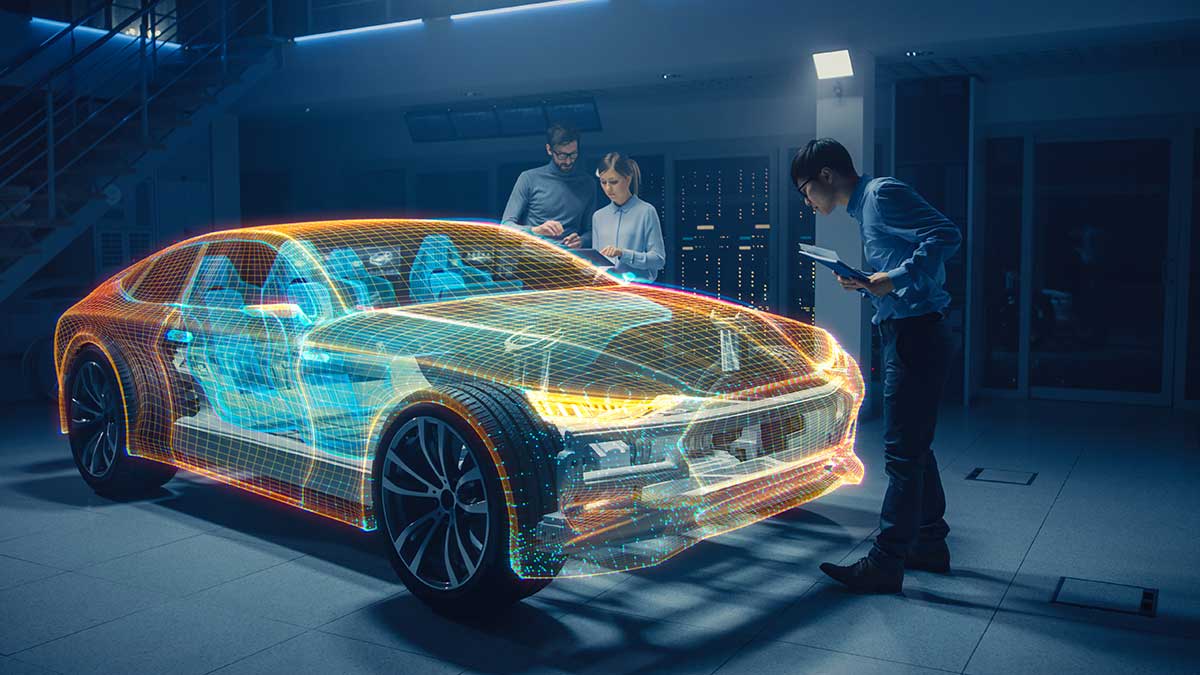
Product design can be extremely complex in some areas of industrial design, such as automotive. For example, Porsche’s process only involves 5 stages, but they are divided into many different tasks. These tasks must be coordinated and proceed in synchrony, as well as combine global vision with minute details, such as the smallest screw in the vehicle.
Porsche’s process also draws attention to the simulation stage. Here, special tools are used so the car’s physical and technical characteristics are played out in a virtual scenario. The goal is to assess the optimal systems and components needed for the vehicle to be safe, functional, and profitable.
This also highlights the importance of tools as key enablers of successful product design. We’ll look into this next.
Which types of tools do product designers use?
Again, this varies from industry to industry. Typically, product design teams use a range of tools, including:
- Journey mapping tools
- Research tools
- Prototyping tools
- CAD tools
- Analytics / testing tools
We can’t forget that in industrial settings, product design is a collaborative process. Therefore, there must be another set of tools that enables all stakeholders to communicate, give and receive feedback. This is even more crucial in teams that work remotely. In these settings, product design teams need tools that allow everyone involved to meet in a virtual space and have access to current project information, beyond the cold environment of a Zoom call.
And here’s another critical thing to note: some tools are specific to stages, functions or even components, as shown in the Skoda Fabia example outlined here. The many tools used in product design aren’t always mutually intelligible, which begs the question: is there a tool that bridges data, communication, and collaboration gaps?
The answer takes us to virtual reality tools, which unify the design process, act as an all-in-one tool and speak a language that all stakeholders understand: an immersive, 3D and visually rich language.
Implementing VR to improve the design process
The potential of VR is so extensive that every stage of product design can benefit from its implementation but still keeping the good aspects of the design process that designers love. Here are some examples:
Development
VR delivers a fully immersive experience where designers can be in the same space as the product and gain insights through means that wouldn’t be available in traditional product design. These insights can substantially transform product development, especially if they’re accurately communicated. Here VR comes in handy too, as this software can help different teams communicate and coordinate their tasks.
Testing
The design process is embedded in uncertainty. Design teams must envision what the market will be like when the final product is ready to launch. Will users still need the product and its current specifications? Testing can help teams adjust concepts based on future predictions, but no forecast is foolproof.
Uncertainty can impact our approach to risk due to the high costs of making mistakes. Since designers can’t account for unforeseen events, what matters is having an agile way of implementing changes and revisions after testing.
VR is well positioned to provide in-process flexibility because it allows for agile change. A VR prototype can be tested and reviewed in the same interface, and changes can be done on-the-fly because:
- There’s no physical model, so there’s no need to waste time and money re-doing prototypes from scratch.
- VR tools like flyingshapes feature a collaborative environment where designers can get test, get feedback, and make changes in real time.
Launch
VR can help present a product in a realistic and appealing way. This has already been done with great success in the automotive industry, with the VR launch of the Ford Mustang Shelby in 2019 or Jaguar’s car launch at Los Angeles Auto Show.
Additional benefits of using VR in product design
- VR software is an excellent validation tool. This article compares VR to a “turbo-charged sketchbook” that enables 3D exploration and validation right from the start. This can help design teams move through the proof-of-concept stage with more certainty.
- Faster time-to-market, since redundant design stages are no longer part of the equation. This is a deal-breaker in industries like automotive, where time-to-market can be as high as 36 months.
- Improved creative freedom, since there’s no need to shy away from variance during the product design process. In VR, mistakes or inaccuracies can be worked on until the product meets all criteria. Liberating designers from the pressure of costly mistakes or time constraints removes the barriers to true excellence.
Conclusion
Product design is a complex process. As such, its success depends on having tools that can address complexity. Virtual reality software is a natural match to the unique requirements of this process. This technology supports communication, collaboration, innovation intelligence, and creative freedom.
Are you a designer or design manager in a studio with more than 15 designers and ready to experience a new way of going about product design? Getting started only takes a few clicks of the mouse. Request your flyingshapes free trial here.